








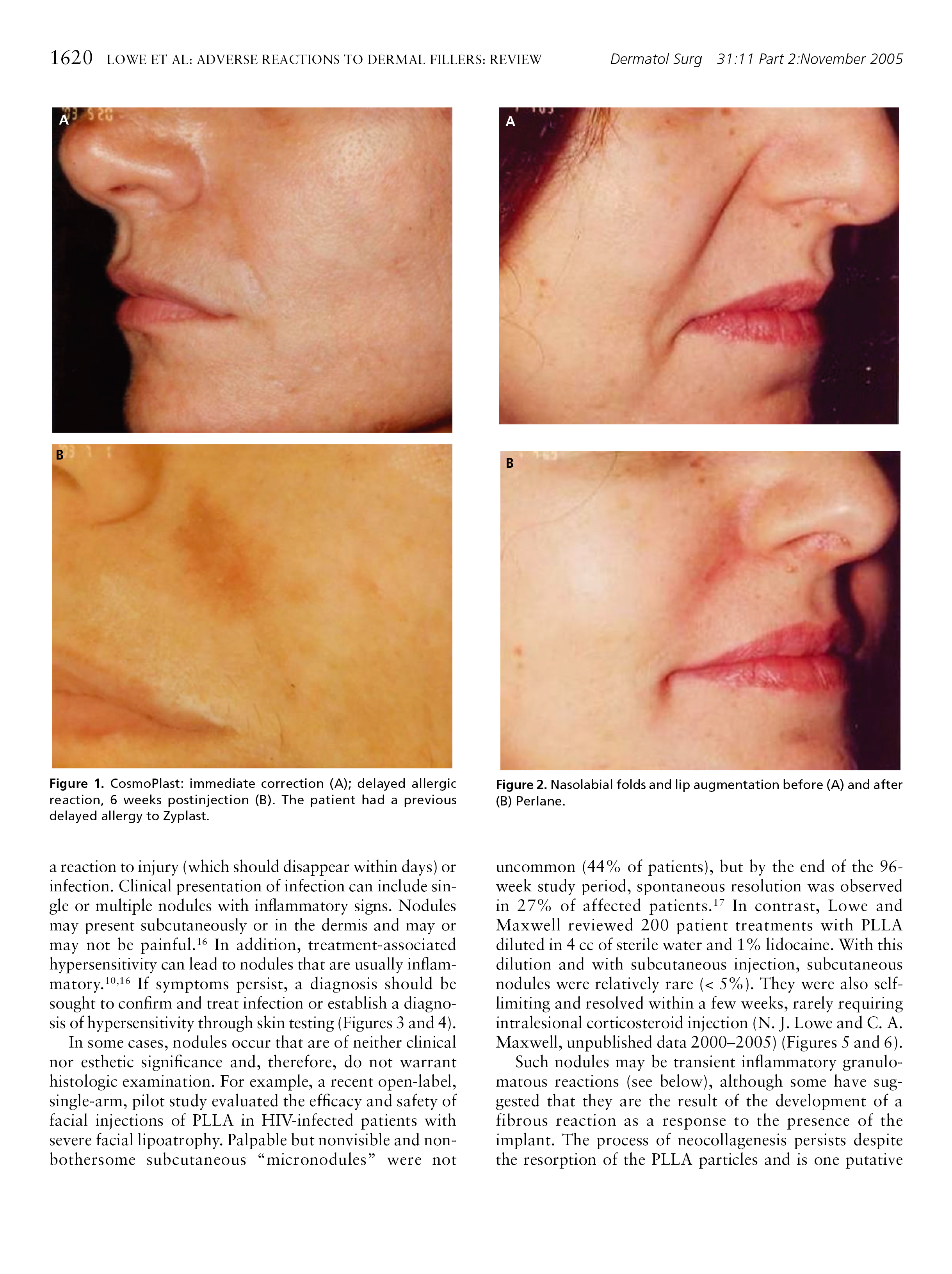

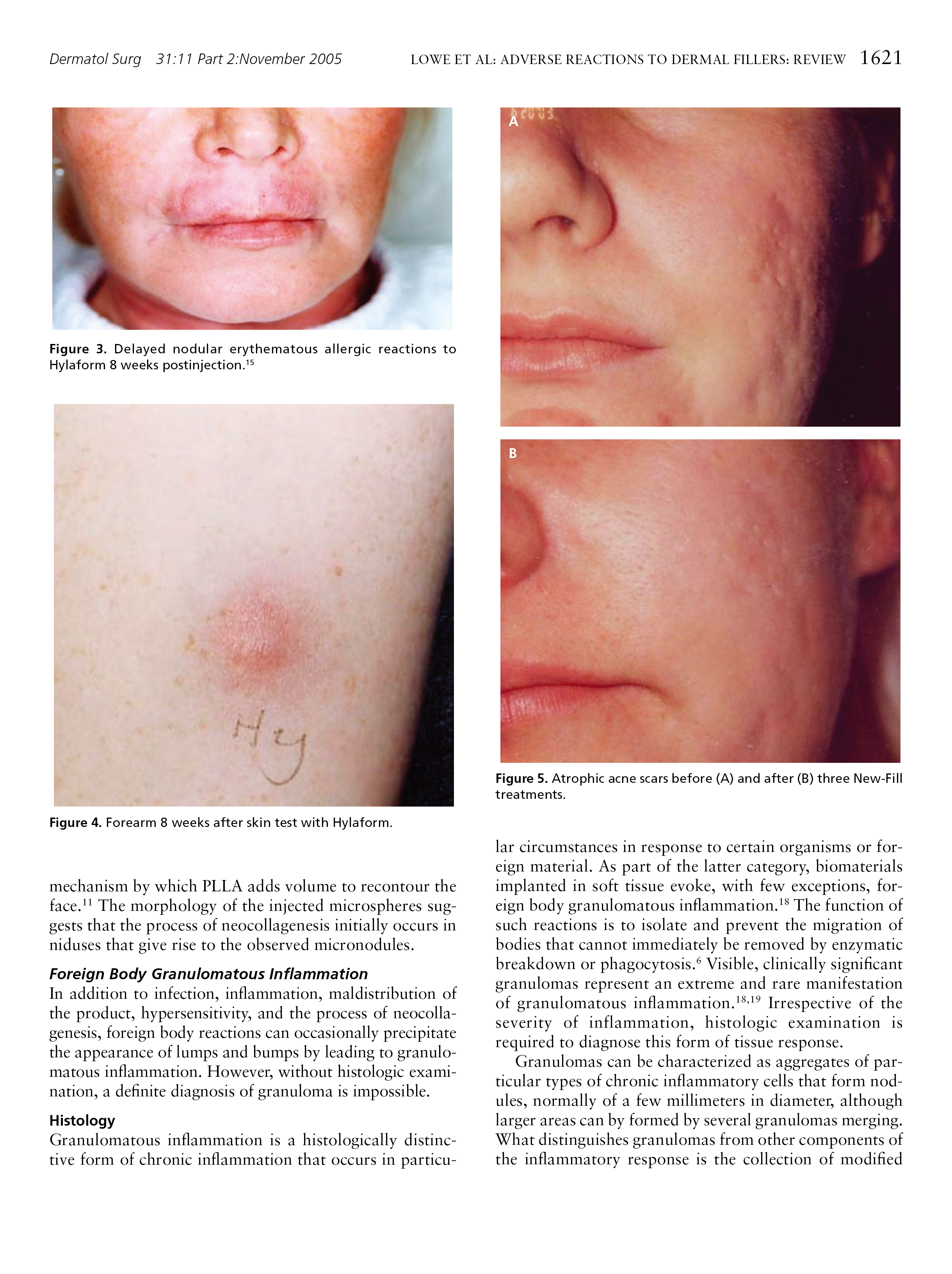




* 特别声明:
1.本栏目所收录的文献,均为已在国内外医学期刊正式发表的学术论文,其内容系独立的科学研究成果。本公司仅作为学术资料进行转载与分享,并不对文献中的观点、数据或结论进行任何形式的背书或确认。
2.本栏目内容仅供相关人士参考,不构成任何形式的医疗建议、产品推荐或治疗方案指引,所有医美项目均需前往正规机构咨询专业医生量身定制合适方案。
3.文献中涉及的医学材料或技术的功效描述,是基于特定学术观点与发现,并非对任何具体产品的功效、安全性或适应症的承诺、保证或宣传。本栏目中涉及的部分医美项目,基于产品特性,请结合所在司法辖区产品注册适应症甄别借鉴。
4.既往研究成果可能被新的科学证据所更新或替代,敬请动态甄别。
5本栏目仅供中国大陆地区年满18周岁用户浏览。

PLLA-induced augmentation is most likely based on capsule formation orchestrating macrophages, (myo-)fibroblasts, and collagen type I and III fibres. We observed considerably slower degradation of PLLA particles than described previously. Thus PLLA partic

Important lessons have been learned in the use of injectable PLLA that have helped reduce the frequency of adverse events and make it desirable for restoring facial volume (Table 1). The importance of diffuse distribution of the injectable PLLA suspension
At the 12-month follow-up, there was a statistically significant increase of skin elasticity and hydration in PLLA-treated subjects and a decrease in transepidermal water loss in both groups. Pigmentation, erythema, and pore size were significantly decre